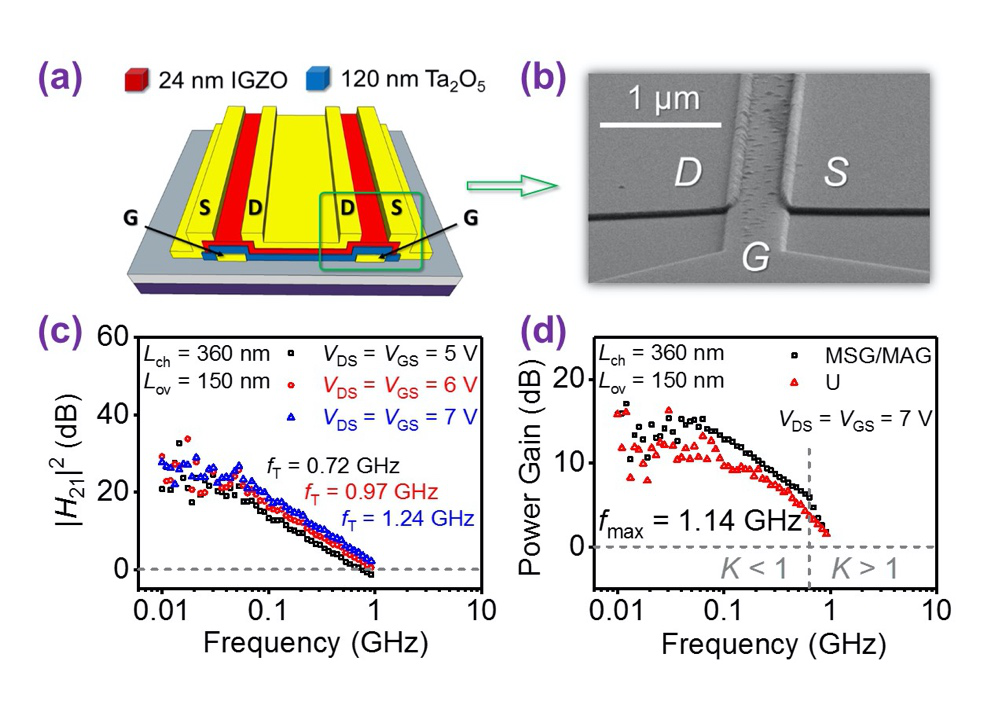
On April 20, 2018, "China Daily" reported on a new progress on high-speed oxide semiconductor thin-film transistors. Qian Xin collaborated with Prof. Song at the University of Manchester and the Institute of Semiconductors of the Chinese Academy of Sciences in this work, and the first author is Wang Yiming at Shandong University. The results have been published online in IEEE Transactions on Electron Device, Vol. 65 (4), 1377-1382, 2018. On April 19, 2018, the international professional media "New Electronics" also reported this achievement with the title "One Step Forward to Flexible TVs and High-performance Wearable Electronics". The cut-off frequency of amorphous indium gallium zinc oxide (a-IGZO) thin film transistors in this work has exceeded 1 GHz, which is equivalent to 1 billion operations per second.
China Daily reported that although traditional silicon transistors have higher electrical performance, they have certain limitations due to their rigidity and opacity. The oxide semiconductor transistor can be flexible and transparent, so it can be used for bendable and transparent display screens, such as new e-books, TVs, wearable devices, and real-time information display on car windshields. Although flexible and transparent oxide thin film transistors have been researched for more than ten years, the previous research has not demonstrated their potential in high-frequency field and 1GHz is a benchmark achievement.
Links to related reports:
http://www.chinadaily.com.cn/a/201804/20/WS5ad8c0cda3105cdcf65195df.html
http://www.newelectronics.co.uk/electronics-news/one-step-closer-to-flexible-tvs-and-high-performance-wearables/172793/?from=timeline&isappinstalled=0