Lung cancer has become the leading cause of cancer death with the highest morbidity among all cancers in the world. Fortunately, the five-year survival rate can increase to 52% if pulmonary nodules can be detected and localized at early stages. Computed tomography (CT), one of the most sensitive imaging modality, is often used to screen pulmonary nodules; and deep learning based classification is considered to be the most promising technology to achieve computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) of pulmonary nodules in thoracic CT images.
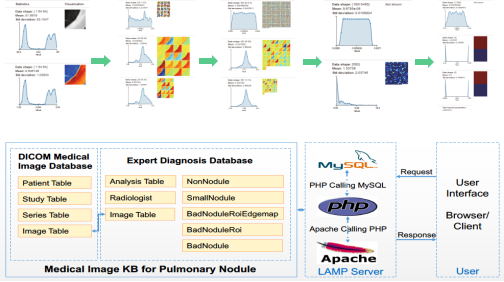
We recently make a trial to implement convolutional neural network (CNN) on the classification of pulmonary nodules in thoracic CT images(Computer-Aided Diagnosis (CAD) of Pulmonary Nodule of Thoracic CT Image Using Transfer Learning. Journal of Digital Imaging. 2019, 32(6): 995-1007). The CT images being involved, obtained from Lung Image Database Consortium and Image Database Resource Initiative (LIDC-IDRI), are reorganized into a medical images knowledge base (KB), which is designed and implemented in our previous work(Design and Implementation of a Medical Image Knowledge Base for Pulmonary Nodules Diagnosis. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer and Communications, 2017, pp 2071-2075). We have performed a two-step classification, not only classifying benign nodules and malignant nodules, but also taking different levels of malignancies into consideration. We have achieved the relatively highest accuracy among related works, and in addition to the high accuracy, we have implemented 10-folder cross validation to test the robustness of our model. We also obtained high sensitivity and specificity as well as good AUC values, which means our model can be very stable. There is no other previous research in nodule classification that achieved such high accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, and AUC values as well as the classification of different levels of malignancies at the same time. We believe that our work is beneficial and has potential for practical diagnosis of lung nodules.
Our work indicates that we can implement the CAD of pulmonary nodules to assist doctors in their pulmonary nodule diagnosis, especially when they come across confusing medical cases, to achieve a higher diagnosis accuracy, and thus improving the survival rate of the lung cancer and potential lung cancer patients.